In brief:
- Healthcare revenue cycle management is challenging because of the industry’s unique and often inefficient processes.
- Healthcare RCM automation vastly increases efficiency, with one organization projecting automating nine common transactions could save the U.S. healthcare system $16.3 billion per year.
- Common challenges must be overcome for successful implementations, including handling revenue cycle process and organizational complexity, limiting siloed automation, and overcoming talent shortages.
- From prior authorization status checks to verification of benefits, revenue cycle automation can save healthcare providers as much as 3.2 million hours of work.
Revenue cycle management (RCM) presents unique and steep challenges. Hospitals, medical device makers, physician groups, and other providers must navigate prior authorizations, claims processing, verifications, and much more to collect revenue and provide quality patient care.
The process is multi-step and complicated by design, and an unspoken tug-of-war between competing revenue cycle management goals underlies it all. Payers may be incentivized to minimize or delay payments while ensuring they are truly necessary, while healthcare providers seek to speed them up—both to manage their revenue cycles and ensure patients get timely care.
Despite these hurdles, there are clear aspects of healthcare’s financial and administrative processes that are ripe for improvement: the painstakingly manual processes that slow everything down. Healthcare revenue cycle management automation can vastly improve the efficiency of prior authorizations, benefits verification, medical billing, and more.
Here is a look at this rapidly evolving technology’s benefits, challenges, and use cases for improving revenue cycle management.
The benefits of healthcare revenue cycle management automation
Examining the pluses of this technology first requires reviewing some of the things it can fix. At the top of this list are healthcare authorizations, claims, and billing involving complicated and often manual steps.
For example, providers must ensure they have complete documentation before seeking prior authorization and submitting claims and then wait for these submissions to be accepted or denied. Personnel in medical facilities’ administrative departments or these institutions’ partners then manually log in to payer portals to check on the status of submissions before they can proceed — sometimes delaying care until approval is noted. In the meantime, a patient’s insurance coverage might change, spurring denials and the need to start over from scratch.
A survey of healthcare financial leaders by the Healthcare Financial Management Association revealed the most significant time wasters:
- 76% reported that denials management was their organization’s most time-consuming task.
- 60% called out prior authorizations.
- Insurance follow-up ranked third, at 58.6%.
Fortunately, while the complexity of insurance and healthcare is unlikely to change anytime soon, the manual nature of these processes can—and is. Automation is a proven and growing strategy for optimizing revenue cycle management functions fraught with frustrating, time-consuming steps.
Automating revenue cycle processes can lower operational costs, boost efficiency, increase productivity without increasing headcount, and centralize critical information and insights for optimized decision-making. In an industry where 80% of healthcare executives struggle with severe labor shortages and turnover, RCM automation can also bridge labor gaps and improve retention by reducing burnout and enabling staff to focus on more interesting and important work.
Consider the following projected benefits:
- The Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare Index (CAQH) recently asserted that fully automating nine common revenue cycle management transactions in areas like claims and insurance verification can save the U.S. healthcare system $16.3 billion.
- A separate CAQH report estimates that automating claims management processes could save healthcare providers nearly $25 billion annually.
- A 2023 paper published by the National Bureau of Economic Research projects that wider adoption of artificial intelligence simplifying and developing healthcare processes could lead to savings of 5-10% in U.S. healthcare spending—roughly $200 billion to $360 billion annually.
- UiPath, the leading intelligent automation platform, projects that automating revenue cycle management processes can save healthcare providers 1.6 million to 3.2 million hours of work (UiPath “The Value of Automating Healthcare Administration Operations” workbook).
RCM Automation in Healthcare for a Better Patient Experience
The challenges facing successful automation efforts
Not everything about healthcare RCM can be automated, of course, and even technology implementations that address clear opportunities must be done right. Deloitte’s 2023 “Global Shared Services and Outsourcing Survey” details many benefits of automation but also some common challenges.
The survey asked business leaders across six industries, including healthcare, about key challenges they’ve faced while implementing automation they wished they’d known ahead of time. The top cited issues were:
- Process and technical complexity — 51%
- Siloed automations — 43%
- Lack of talent — 40%
- Defining ownership and accountability — 33%
- Scattergun (unorganized) approach to automation — 33%
Most of these issues are tied to disorganized planning and implementations. Implementing revenue cycle management automation and similar technologies demands clearly defining target processes, individual roles and responsibilities, data-sharing protocols, and more.
Many healthcare organizations lack the expertise or resources to implement in-house solutions, so they turn to outsourcing providers. In these cases, it’s essential to vet external partners carefully and ensure they are familiar with your industry and their solutions have a proven track record.
In addition, RCM automation providers must do the work upfront, taking the time to methodically map processes and roles, followed by guiding clients through implementation and usage. Failing to do so can result in new inefficiencies, even when the goal is to sunset old ones.
For example, automation siloing happens when multiple departments, data sources, touchpoints, and automation practices fail to work together, creating inconsistencies and poor business continuity. Deloitte’s survey revealed that siloed automations were the main challenge among the 34% of organizations that only achieved less than 10% in savings from their automation efforts.
Successful automation implementations account for these challenges by identifying the best items to automate, building a roadmap to do it, and scaling as needed while ensuring process visibility and integration. Whether RCM automation is an in-house or outsourced effort, it demands an organized, systematic approach.

5 key healthcare RCM automation use cases
Automation can’t eliminate the complexity of navigating medical payments and care, but it’s exceptionally valuable for managing crucial aspects of the process. The technology is particularly good at tackling manual steps that waste skilled personnel’s time while helping lower overhead and get patients the care they need faster.
The rise of intelligent automation and Generative AI (GenAI) are also paving the way for a more streamlined and accurate approach to managing healthcare finances – combining advanced algorithms, machine learning, and predictive analytics to influence revenue cycles and improve operational efficiency.
Here’s an overview of some of the best use cases for healthcare RCM automation:
1. Patient registration and eligibility verification
Healthcare revenue cycle management starts with the initial point of contact with patients: registration. And thankfully, paper-based registration processes involving filling out redundant forms and photocopying insurance cards are becoming a thing of the past.
Digital intake from various points (e.g., patient portals, smartphones, or kiosks) and automated processes combine to save time, hassle, and paper. These processes mitigate or eliminate manual data entry errors while streamlining scheduling.
Robotic process automation (RPA) and AI can simultaneously verify a patient’s eligibility for services, prescriptions, and more, automatically cross-referencing insurance information against the portals of hundreds of public and private payers.
Leveraging AI-powered automation to ensure providers have the most up-to-date and accurate information concerning insurance coverage, deductible amounts, co-pays, and other relevant details delivers considerable ROI – helping to reduce claim denials and improve cash flow. Real-time verification also enables healthcare providers to spot eligibility issues and address them before non-emergent services are rendered.
2. Prior authorization information gathering and status checks
Obtaining prior authorization for medical services, prescriptions, and equipment is one of the lengthiest and most error-prone processes in healthcare, with many unnecessarily manual steps. Providers must submit prior authorization documents correctly the first time or face denials, and staff typically manually access payer portals multiple times to check on status.
The number of prior authorization requests a medical provider manages at any given time would take a massive number of humans logging into portals every single day to verify access to medically necessary care as fast as possible.
Robotic process automation and AI fix many of these inefficiencies that cause billing and care delays. Automated intelligent document processing leveraging machine learning can review prior authorization packages to ensure providers have all necessary information, including medical records documentation, physician letters, lab results, and more, before automatically submitting packages to payer portals. The process drastically lowers rejections and resubmissions due to human error.
Automation also eliminates manual prior authorization status checks by compiling a list of pending orders from electronic medical records (EMR) systems and logging into payer portals to check on them. These verifications are some of the biggest time-savers healthcare automation offers, often speeding up patients’ access to care significantly.
UiPath’s workbook estimates that automating these activities alone can save healthcare providers’ RCM staff up to 33,000 hours of work.
3. Submitting accurate claims and avoiding denials
Even with prior authorization, claim submissions involve manual steps prone to potential errors and unnecessary delays. Intelligent automation streamlines the end-to-end claims management process, from creation and submission to denial resolution. Besides expediting reimbursement, automation also significantly reduces billing errors found in a whopping 80% of medical bills, which prompt half of insurance denials, according to the Professional Medical Billers Association (PMBA).
More than 25% of insurance denials are due to typos, PMBA reports. Simple errors like blank fields, incorrect plan codes, and technical mistakes like missing modifiers also trigger rejections.
Unfortunately, even small errors can have big consequences. The cost of reworking or appealing denials: an average $25 per claim for practices and $181 per claim for hospitals, according to a Journal of AHIMA (American Health Information Management Association) report.
The best defense against the financial damage of denied claims is improving claim accuracy with automation. Machine learning algorithms can crunch vast amounts of historical claims data to pinpoint patterns and predict the likelihood of denials – helping RCM teams implement strategies that minimize rejections.
Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms combined with GenAI can review clinical documentation and coding to ensure compliance with coding guidelines, reducing the risk of denials due to coding errors. Automated scripts can proactively review claims for other common issues before submission; for instance, looking for missing information, spotting the need for additional supporting documentation, and even detecting fraudulent activity.
By this point, the automated system has already verified what entity has the primary payment responsibility and any supplemental insurers based on the patient’s eligibility. Thus, automation can also assist in submitting claims, checking their statuses in payer portals, and other time-draining follow-up tasks that prevent human staff from focusing on more value-add work.
4. Managing denials
Claims denials are a constant challenge for healthcare providers – increasing revenue cycle complexity, delaying reimbursement, and decreasing profitability. Nearly 20% of claims are denied by insurance payers – and up to 60% of returned claims are never resubmitted, the Journal of AHIMA report states.
Unresolved claim denials represent an average loss of $5 million for hospitals, the Journal of AHIMA reports. As bottom-line pressures mount, that’s up to 5% of net patient revenue.
AI-powered automation empowers organizations to realize process improvements that not only reduce denials on first submission but also create more efficient ways to handle them when they occur. With a significant portion of denial management ripe for automation, healthcare providers can eliminate the need to weigh the substantial cost of manually recovering payments against the amount received.
For example, RPA can track disparate deadlines for resubmissions and appeals among different payers and classify and route denials properly. AI-powered automation can analyze kicked-back claims based on specific claim adjustment reason codes (CARC), check insurance benefits, verify eligibility, and determine a resolution approach. It can also repeat many of the same error-catching steps in the prior authorization and claims submissions processes.
The combination of GenAI, RPA, user interfaces (UI), and application programming interfaces (API) supports end-to-end process improvements. For example, using RPA to extract relevant data from medical records so GenAI has the context it needs to craft detailed appeals letters. RPA can then upload and submit the completed documents.
5. Accounts receivable management
Automation also adds value to accounts receivable (AR), including collecting payments from payers and patients. RPA will post payments into the electronic health record (EHR) system while merging data from different payment sources, detect claim underpayments, reconcile transactions with statements, and more.
Automation can generate patient statements through portals and apps, plus help manage late payments and bad debts by aiding decisions about payer statuses based on an organization’s policies. Predictive analytics can forecast revenue patterns and identify risks that help organizations proactively implement strategies to maximize revenue generation and minimize leakage.
AI-driven analytics can also assess patient financial data, predict potential payment issues, and offer personalized guidance to reduce the likelihood of defaults.
AR is one of the most popular automation applications across a range of industries, including healthcare, because of its realized efficiency benefits. The Shared Services & Outsourcing Network’s (SSON) “AR Pulse Check Survey” revealed that almost 60% of finance leaders say replacing manual, repetitive tasks with automation is their top AR priority. This technology is a powerful tactic for speeding payments and reducing days sales outstanding (DSO)—the bane of AR departments and the entire revenue cycle management process.
AI can provide revenue optimization insights as well – analyzing immense amounts of data like payer trends and reimbursement patterns to uncover opportunities for optimizing pricing strategies, renegotiating payer contracts, and more.
See the larger scope of healthcare RCM automation services and touchpoints in this process map from UiPath:
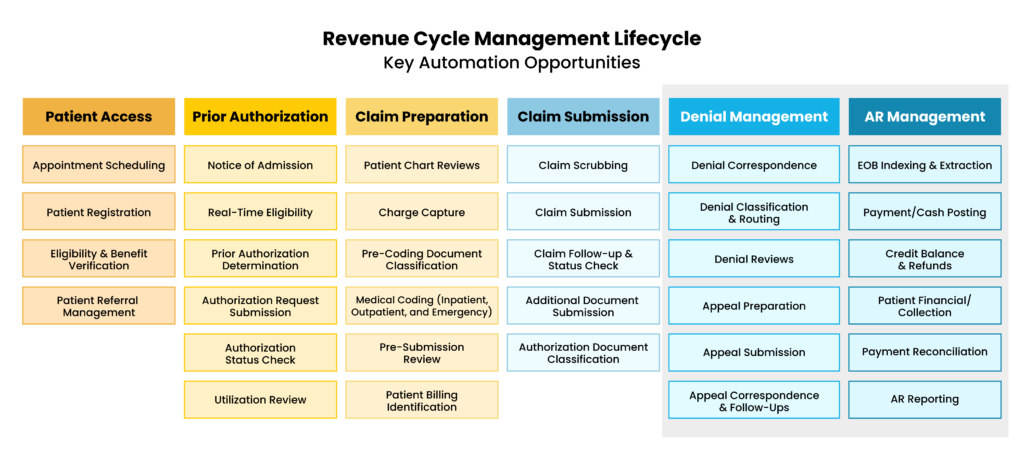
Successful healthcare RCM automation depends on the right plan, implementation, technology, and partner
Automation presents a massive opportunity to streamline a healthcare organization’s RCM efforts. The technology makes sense of disparate data sources and eliminates time-consuming manual steps, many of which are unique to the healthcare industry.
Nevertheless, despite the tremendous benefits of RCM automation, some organizations struggle with successful implementations that realize this potential. For example, McKinsey’s “Automation Survey” found that over half of responding institutions consider their programs “much harder to implement than they expected.”
Successful initiatives depend on first identifying the best automation opportunities and creating a roadmap to achieve them, followed by implementing an efficient, effective program that maintains the ability to scale. At the center of all of this must be a quality and proven RPA platform. And when it comes to healthcare, implementations require solutions and partners to be intimately familiar with the unique challenges of this industry.
Auxis is a knowledgeable outsourcing provider with deep experience helping healthcare organizations reap the benefits of this technology. We are a Platinum Partner for the #1 intelligent automation platform UiPath—its highest partnership level—and our nearshore Center of Excellence lowers costs while providing more than 150 top-quality, certified UiPath developers with deep experience navigating the complexities of RCM automation.
See some of the impacts of Auxis’ healthcare RCM automation solutions by reading this case study, where we helped a leading medical supplier reduce workloads while achieving faster revenue collection and patient service. You can also learn more about our digital strategy consultation, intelligent automation, and revenue cycle management outsourcing services, or simply schedule a consultation today!



